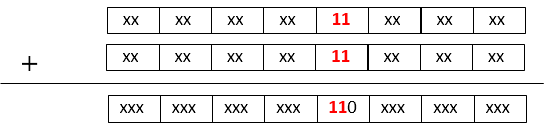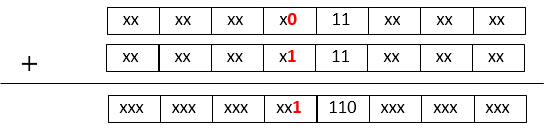Regarding CSA[1]
- Normally addition is from LSB and carry is added to the next bit and calculated until the final MSB and there is possibility that carry will be propagated to MSB delaying the calculation by the amount. To speed up addition, following methods are available but most only speed up one addition.(Each detail as below)[2]
- Carry look-ahead adder
- Carry select adder
- Carry skip adder
- Carry save Adder
- Hybrid addr (combination of above)
- Carry save adder(hereafter CSA) saves the carry generated by the computation of each bit separately so that carry is not propagated to the next bit inhibiting delay in calculation, but need to return carry and value stored separetely to its original type to resolve the carry so there may not be much merit. For example addition by CSA each digit is added twice so independent of number of bits, delay is 2, as when returning carry to resolve it to normal value delay will be as much as number of bits.
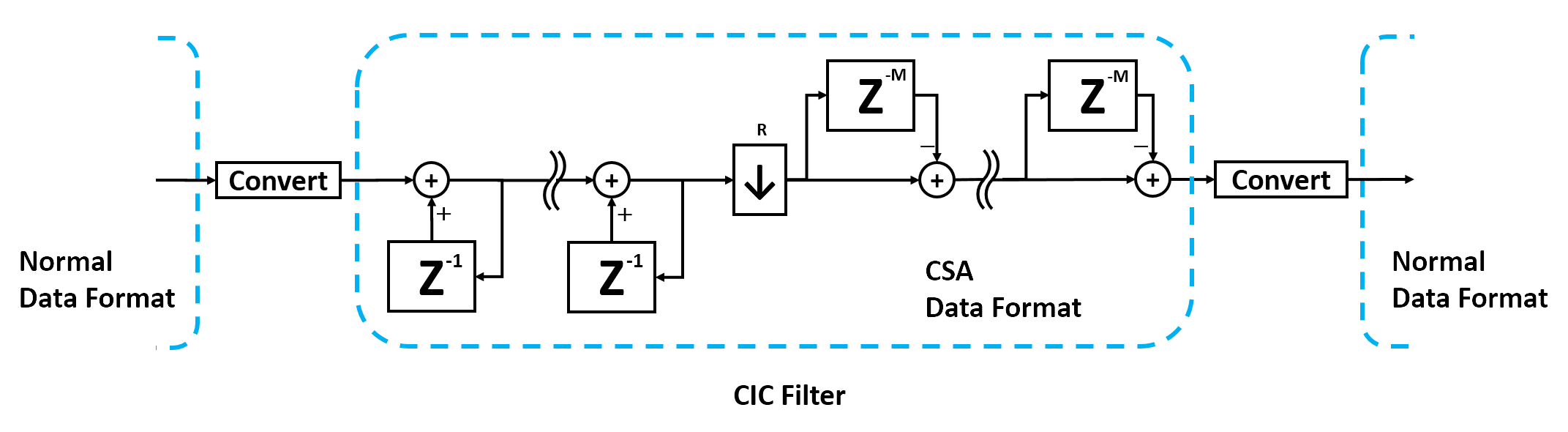
- However, for filter operation such as CIC Filteraddition to previous addition result is performed continuously in which case CSA is excellent. CIC filter is a cascade of integrator and differentiator, and if addition result from the previous stage can be used in CSA type without having to return it to normal type then speed operation can be achieved. Can return to normal only at the end of CIC filter.
Outline of CSA
- Will explain about CSA calculation method. With CSA will set so that Carry does not propagate higher and each digit has a Carry. So that for each digit will have 2 bits one for Value and one for Carry.
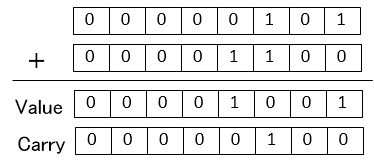
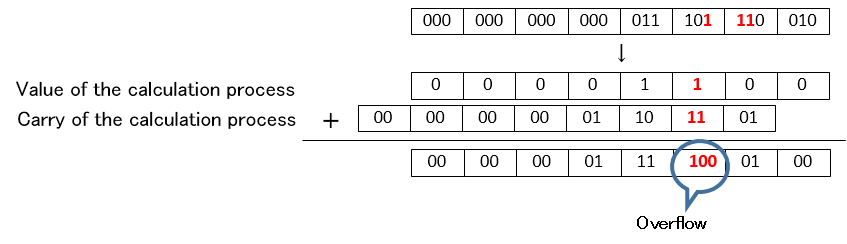
For example
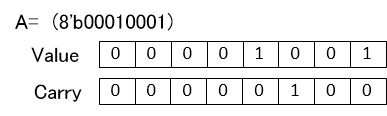
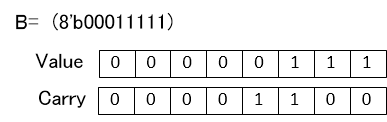
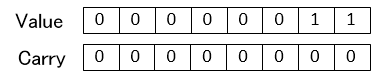
A=8'b00000101
B=8'b00001100
when addition of (A+B) is performed, will keep it as Carry and not reflected in Value or Carry as below
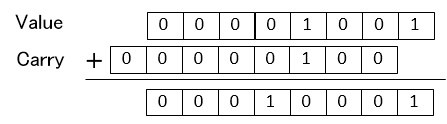
Like this in CSA type numbers are expressed by Value and Carry. When returning CSA type value to normal value and reflecting it as Carry, then Carry is left shifted by 1 and added to Value.
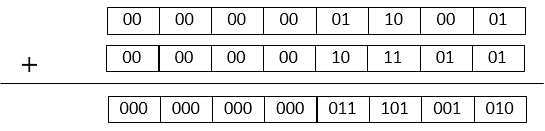
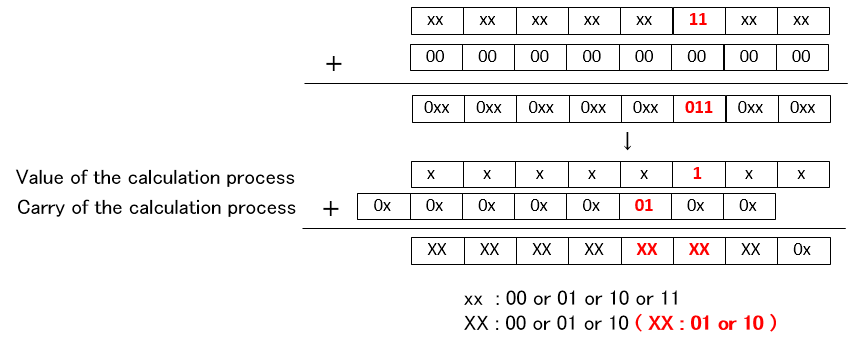
Next will explain about mutual CSA type addition. Will assume A,B with value of result Carry which has been CSA type calculation repeatedly. 2 bits packing each digit Value and Carry to be data
First each digit 2 bit data is added to give intermediate result. 2 bit is added to 2 bit so that the intermediate result is each digit 3 bits.
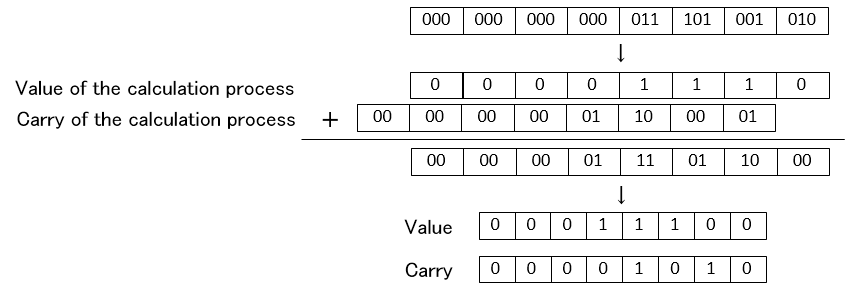
This result is ordered into Value and Carry. Each digit intermeduate result upper 2 bits is carry to next digit so upper 2 bits of previous digit and lower 1 bit of the same digit which is Value is added as follows
Thus propagation of Carry for 1 addition is performed only once. Using this method normal type value is added to make CSA type and then that CSA type value is added.
Overflow problem of CSA
- As explained till now, addition of CSA is 2 bit operation dividing Value and Carry. When a value which is not of CSA type is transformed to CSA type and used for calculation then there will not be a carry and overflow will not occur, but if the calculation is using both CSA type values then there is a possibility of an overflow occuring.
For example, value A and value B each digit when added then the 3 bit result can be as follows
and the 3rd digit is overflowing. Normally this needs to be propagated to another higher digit. But if this is propagated then the merit of CSA will be diluted.
Analyzing overflow shows that it occurs when it is xx111x. This means that it occurs when value A and B to be added have condition as follows which is true.
- When Value and Carry both are 1 for N digit of both A and B
- When Value of either A or B's Nth+1 digit is 1 and the other is 0
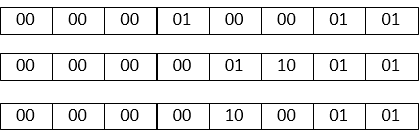
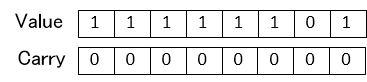
Consider if there is not a method to ensure that 1. and 2. conditions do not overlap. For CSA type even for the same value, several expressions exist as below(All are the same value 8'b00010011)
Of course when Carry is all 0 then there is no problem, but that means that all Carrys have to be resolved and need to return to normal type. Tried to create an expression whereby Carry need not be resolved and there is no overflow condition. Will see if by not changing the value and propagating Carry only one more time, will allow overflow condition to be bypassed. Which is to say will add 0. As below 0 is added to value of condition 1.
Result is that both Value and Carry are not 1 and clears the condition of 1. From this we know that by adding 0 to the result from CSA, overflow can be avoided. An additional add operation is there but compared to propagating Carry for all digits using normal type speed is achieved.
Subtraction using CSA
- Next will consider subtraction. Previously mentioned CIC filter's differentiation module requires subtraction. In normal subtraction complement of 2 is added.
For example
8'b00001000 − 8'b00000011 = 8'b00000101
Complement of 2 is 2^N bit - value.
9'b100000000 − 8'b00000011 = 8'b11111101
That is reversal + 1. Subtraction above is achieved by adding complement of 2
8'b00001000 + 8'b11111101 = 8'b00000101
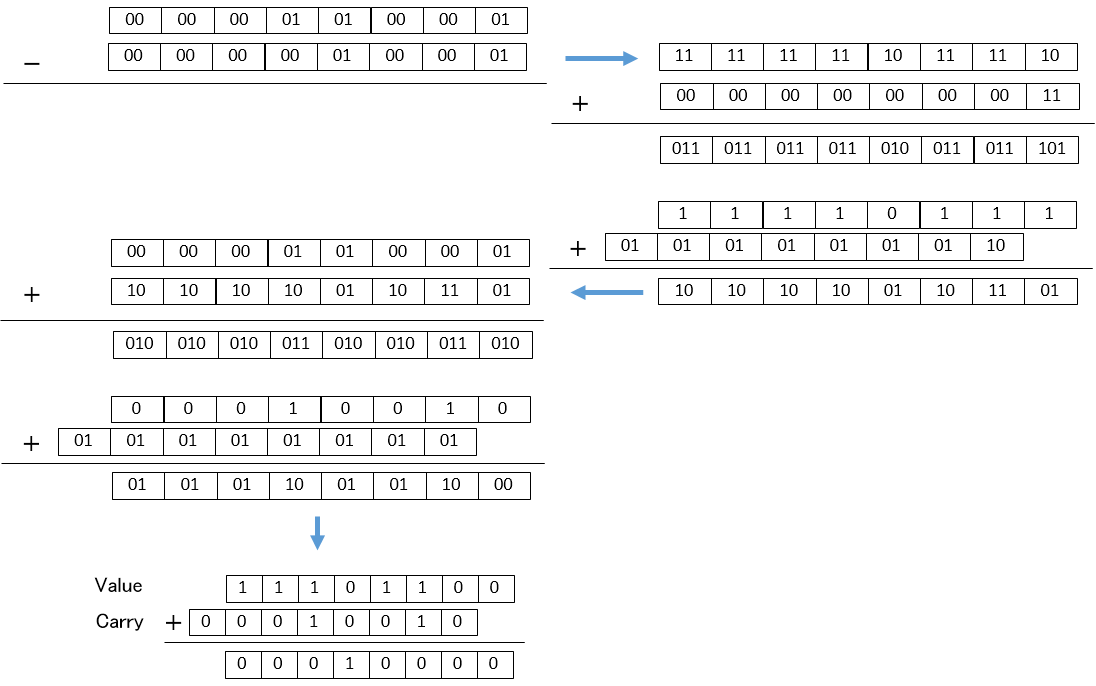
- Here when 8'b00000011 is expressed as CSA
Complement of 2 8'b11111101 is expressed as CSA
and both Value and Carry are reversed and both Value and Carry are +1. In CSA type Value and Carry are packed so it is convenient to reverse Value and Carry together.
- For example
8'b00011001 − 8'b00001001 = 8'b00010000
is calculated. When calculated using CSA type
and can say that subtraction can also be achieved using CSA type.[3]
CSA Code
/* **************************** MODULE PREAMBLE ********************************
Copyright (c) 2012, ArchiTek
This document constitutes confidential and proprietary information
of ArchiTek. All rights reserved.
*/
// ***************************** MODULE HEADER *********************************
//
// Module for adding normal type value and CSA type value
// CSA type value+normal type value=CSA type value
//
module CSA (
iA,
iB,
oY
);
// ************************ PARAMETER DECLARATIONS *****************************
parameter W = 4; // Normal type bit width
// *************************** I/O DECLARATIONS ********************************
// Input
input [W*2-1:0] iA; // CSA type input value A
// Bit width is twice normal type
input [W-1:0] iB; // Normal type input value B
// Output
output [W*2-1:0] oY; // CSA type output value
// Bit width is twice normal type
// ************************** LOCAL DECLARATIONS *******************************
// ****************************** MODULE BODY **********************************
//Actual operation is thru CSAFunc
assign oY = CSAFunc(iA, iB);
// ************************** FUNCTIONS and TASKS ******************************
function [W*2-1:0] CSAFunc;
input [W*2-1:0] opA;
input [W-1:0] opB;
reg [1:0] result[0:W-1];
reg [1:0] tmp;
integer i;
begin
// 0 bit addition result is inserted into result
// No Carry for 0 bit
result[0] = {1'd0, opA[0]}
+ {1'd0, opB[0]};
// 1 bit and higher addition results are inserted into result
// For 1 bit and higher previous bit Carry and Value A and B values are added.
for (i=1; i < W; i=i+1)
result[i] = {1'd0, opA[i*2-1]}
+ {1'd0, opA[i*2]}
+ {1'd0, opB[i]};
// result is inserted as CSA type
for (i=0; i < W; i=i+1) begin
tmp = result[i];
CSAFunc[i*2+1] = tmp[1];
CSAFunc[i*2] = tmp[0];
end
end
endfunction
endmodule
// *****************************************************************************
CSA Type ⇔ Normal type transform code
- When calculating normal type value after tranforming to CSA type or, when returning CSA type result to normal type the below function is embedded and used.
//
// Function to transform normal type value to CSA type
//
function [CSA_BIT_W-1:0] bin2csaFunc;
input [BIT_W-1:0] data;
integer i;
begin
for(i=0 ; i < BIT_W ; i=i+1) begin
bin2csaFunc[i*2] = data[i]; // Insert value into Value part
bin2csaFunc[i*2+1] = 1'b0; // Insert 0 into Carry part
end
end
endfunction
//
// function to transform CSA type value into normal type value
//
function [BIT_W-1:0] csa2binFunc;
input [CSA_BIT_W-1:0] data;
reg [BIT_W-1:0] carry;
reg [BIT_W-1:0] value;
integer i;
begin
for (i=0; i < BIT_W; i=i+1) begin
carry[i] = data[i*2+1]; // Extract Carry part
value[i] = data[i*2]; // Extract Value part
end
// Carry part is shifted 1 bit to the left and added to Value
csa2binFunc = {carry[BIT_W-2:0], 1'b0} + value;
end
endfunction
Logical circuit design > Technic > Fast operation Next page(Pipeline feedback) TOP of this page ▲